The Eternal Celestial Partnership
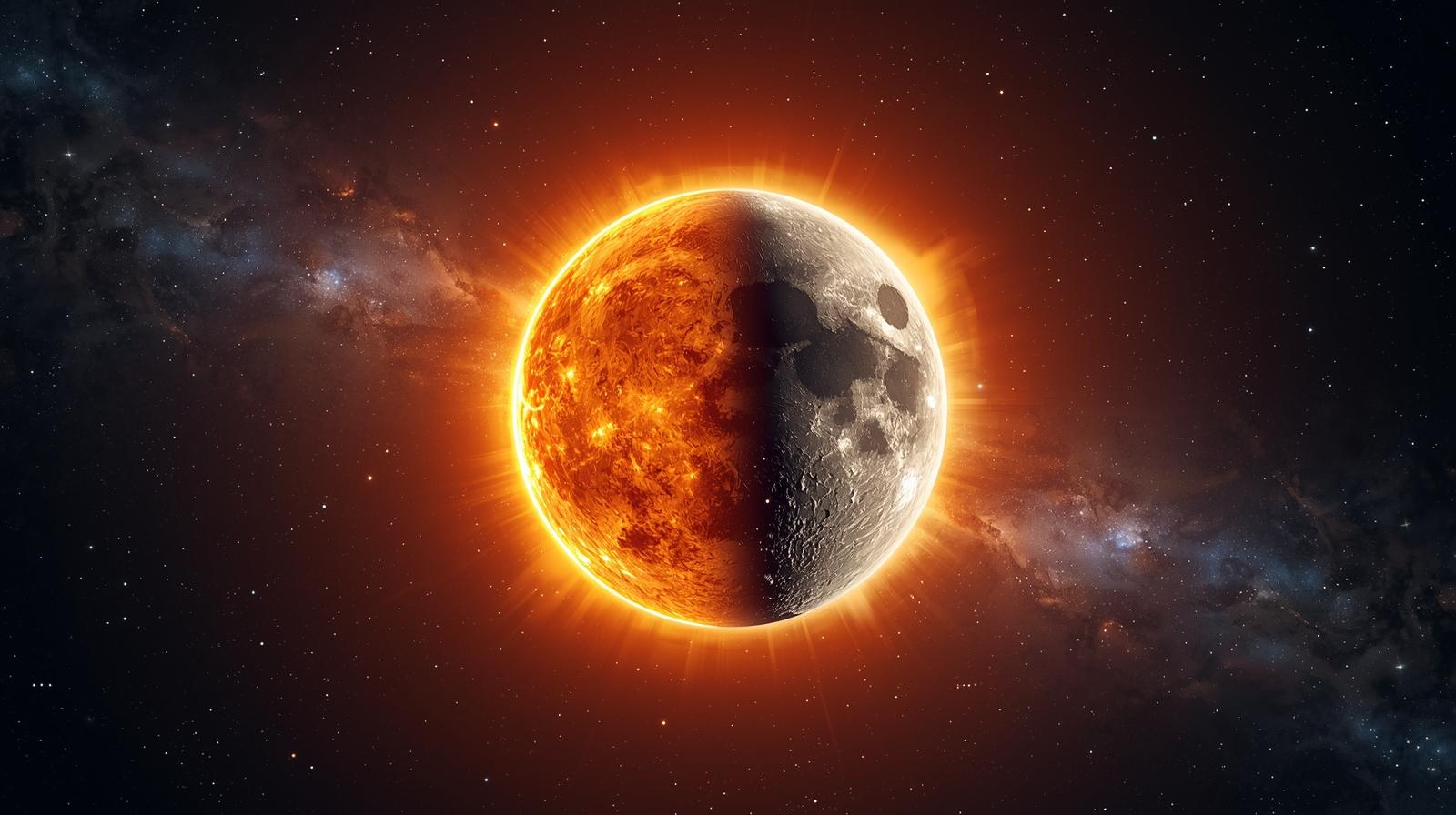
Have you ever looked up at the sky and wondered why the sun and moon appear nearly identical in size, even though one could swallow the other millions of times over? This cosmic coincidence has fascinated humanity for millennia, shaping our myths, calendars, and understanding of the universe itself.
The sun vs moon debate isn’t really a competition it’s a story of complementary forces that govern life on Earth. While the sun blazes as our life-giving star, the moon serves as Earth’s faithful companion, orchestrating tides and illuminating our nights. Together, they create the celestial rhythm that has captivated cultures across every continent.

Table of Contents
Understanding Our Star and Satellite
The Sun: Life’s Powerhouse
The sun contains 99.8% of our solar system’s mass and serves as the gravitational anchor keeping planets in their orbits. This massive ball of hydrogen and helium generates energy through nuclear fusion in its core, where temperatures reach about 27 million degrees Fahrenheit.
The sun’s diameter spans approximately 865,000 miles so immense that it could contain roughly 1.3 million Earths. Yet from our vantage point 93 million miles away, it appears as a modest disk in the sky, approximately the same apparent size as our moon.
The Moon: Earth’s Ancient Guardian
Our moon, by contrast, measures a mere 2,159 miles in diameter small enough that the sun is roughly 400 times the size of the moon. Formed approximately 4.5 billion years ago, likely from debris created when a Mars-sized object collided with early Earth, the moon has been our constant companion throughout human history.
The temperature on the moon reaches about 260 degrees Fahrenheit when in full sun, but in darkness, temperatures plummet to about -280 degrees Fahrenheit. This extreme temperature variation occurs because the moon lacks a substantial atmosphere to regulate heat.
The Perfect Cosmic Coincidence
Why Sun vs Moon Appears Equal
Here’s where the sun vs moon comparison becomes truly remarkable. The sun, which is roughly 400 times the size of the moon, also just happens to be roughly 400 times further away. This extraordinary alignment means both celestial bodies appear nearly identical from Earth’s surface a coincidence that occurs nowhere else in our solar system.
This precise alignment enables one of nature’s most spectacular phenomena: total solar eclipses. When the moon passes between Earth and the sun, it fits perfectly over the sun’s disk, temporarily blocking its light and revealing the sun’s ethereal corona.
A Temporary Wonder
The moon’s gradual recession from Earth, caused by tidal interactions, will eventually result in only annular solar eclipses being observable in approximately 50 million years. Currently, the moon drifts about 38mm (1.5 inches) away from Earth annually. This means we’re living in a rare window of cosmic time when total solar eclipses are possible a privilege our distant ancestors and future descendants won’t share.
Composition and Physical Properties
| Property | Sun | Moon |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | ~865,000 miles | ~2,159 miles |
| Mass | 1.989 × 10³⁰ kg | 7.342 × 10²² kg |
| Surface Temperature | ~5,772 K (9,932°F) | -280°F to 260°F |
| Core Temperature | ~27 million°F | Likely 2,280°F – 2,520°F |
| Composition | 91% hydrogen, 8.9% helium | Rocky (silicate rock and metal) |
| Distance from Earth | ~93 million miles | ~239,000 miles |
| Age | ~4.6 billion years | ~4.5 billion years |
Energy and Light
The fundamental difference in the sun vs moon comparison lies in their relationship with light. The sun generates its own energy through nuclear fusion, converting hydrogen into helium and releasing massive amounts of electromagnetic radiation. This process has continued for billions of years and will persist for billions more.
The moon, conversely, produces no light of its own. What we perceive as moonlight is actually reflected sunlight bouncing off the moon’s rocky, crater-pocked surface. This reflected light provides just enough illumination to transform night into a silvery twilight rather than pitch darkness.
Cultural and Mythological Significance

Ancient Perspectives on Sun vs Moon
Throughout human history, the sun and moon have embodied fundamental dualities: masculine and feminine, day and night, conscious and unconscious. These celestial bodies weren’t merely astronomical objects to our ancestors they were deities, storytellers, and cosmic forces that shaped religious practices and daily life.
In Chinese culture, the sun and moon hold profound significance, embodying the dualities of light and darkness, activity and passivity, and the cyclical nature of life. The famous legend of Chang’e, the Moon Goddess, and her husband Hou Yi illustrates the eternal separation between sun and moon, a metaphor for unattainable love and cosmic balance.
In Aztec mythology, Tonatiuh (the sun) and Metztli (the moon) represented the dualities of nature, from day and night to life and death. The Aztecs believed these celestial bodies engaged in an eternal cosmic dance, requiring human sacrifice to ensure the sun’s continued journey across the sky.
Personal Reflection on Celestial Wonder
I’ll never forget the first time I witnessed a total solar eclipse. Standing in the path of totality, watching the moon slowly consume the sun until only a brilliant corona remained, felt like witnessing the universe’s greatest magic trick. In that moment, the sun vs moon relationship transformed from abstract knowledge into visceral reality two celestial bodies, impossibly different in size and nature, aligned with such precision that they appeared as one.
That experience taught me something our ancestors understood intuitively: the sun and moon aren’t competitors but partners in an eternal dance. They represent balance rather than opposition, demonstrating that even the most disparate forces can work in harmony.
Impact on Earth and Life
The Sun’s Life-Giving Role
Without the sun, Earth would be a frozen, lifeless rock drifting through space. Solar radiation drives photosynthesis, enabling plants to convert light into chemical energy that fuels entire ecosystems. The sun’s heat creates weather patterns, ocean currents, and climate zones that make diverse life possible.
The sun’s influence extends beyond mere illumination. Solar storms and flares can impact satellite communications, power grids, and even aurora displays. The 11-year solar cycle affects everything from radio communications to climate patterns, reminding us that we live within our star’s sphere of influence.
The Moon’s Subtle Influence
While less dramatic than the sun, the moon’s influence permeates Earth in subtle yet significant ways. Lunar gravity creates tidal bulges in Earth’s oceans, generating the twice-daily tides that have shaped coastal ecosystems and human civilizations for millennia. These tidal forces also gradually slow Earth’s rotation, lengthening our days by about 1.7 milliseconds per century.
The moon stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, preventing dramatic climate swings that would make complex life difficult or impossible. Some science researchers suggest this stability was crucial for allowing life to evolve and thrive on our planet.
Modern Scientific Understanding
Observing Sun and Moon Today
Modern technology has revolutionized our understanding of the sun vs moon relationship. NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter continuously maps the moon’s surface, while solar observatories like the Solar Dynamics Observatory monitor our star’s activity in unprecedented detail.
Several spacecraft are currently investigating the sun including Parker Solar Probe, STEREO, Solar Orbiter, SOHO, Solar Dynamics Observatory, Hinode, IRIS, and Wind. These missions reveal the sun as a dynamic, ever-changing plasma ball rather than the static yellow circle we see from Earth.
The moon, too, continues surprising us. Recent discoveries have confirmed water ice in permanently shadowed lunar craters, changing our understanding of the moon’s resources and potential for future human exploration.
Future Exploration
Both celestial bodies remain priority targets for scientific exploration. NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the lunar surface, establishing a sustainable presence that could serve as a stepping stone for deeper space exploration. Understanding the sun’s behavior grows increasingly important as our technological civilization becomes more vulnerable to solar storms.
For more fascinating insights into celestial phenomena, check out Ninty2magazine for cutting-edge astronomy coverage.
The Sun vs Moon in Daily Life
The sun vs moon dynamic shapes human experience in countless ways. Our circadian rhythms evolved in response to the sun’s daily cycle, programming sleep-wake patterns into our biology. The moon’s phases inspired the concept of months and influenced agricultural practices, hunting, and fishing traditions worldwide.
Even today, solar and lunar cycles affect modern life. Solar panels harness the sun’s energy to power homes and businesses, while the moon’s gravitational influence remains crucial for coastal navigation and ecosystem management. The sun and moon appear in art, literature, poetry, and music, serving as eternal metaphors for opposing yet complementary forces.
Key Differences Between Sun and Moon
When examining sun vs moon characteristics, several fundamental distinctions emerge:
Energy Source: The sun generates its own energy through fusion, while the moon reflects sunlight.
State of Matter: The sun exists as plasma and gas, while the moon is solid rock and regolith.
Gravitational Influence: The sun’s gravity governs planetary orbits, while the moon’s gravity creates Earth’s tides.
Surface Conditions: The sun’s surface churns with solar storms and magnetic phenomena, while the moon’s surface remains static, marked only by ancient impacts.
Lifespan: The sun will eventually expand into a red giant, consuming inner planets. The moon will drift away until it appears smaller than the sun, ending total solar eclipses.
Conclusion
The sun vs moon relationship represents one of nature’s most beautiful coincidences two celestial bodies, vastly different in nearly every measurable way, appearing identical from our earthly perspective. This cosmic alignment has enabled countless total solar eclipses throughout human history, inspiring wonder and driving scientific inquiry.
Understanding the sun and moon means appreciating both their differences and their complementary roles. The sun provides energy and defines our days, while the moon stabilizes our planet and marks our nights. Together, they create the celestial framework within which all terrestrial life exists.
As we continue exploring these ancient companions with modern technology, we uncover new mysteries while deepening our appreciation for the forces that make Earth habitable. The sun vs moon story isn’t about which is superior it’s about recognizing how profoundly both shape our world and our understanding of the cosmos.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why do the sun and moon look the same size in the sky?
The sun is approximately 400 times larger than the moon but also roughly 400 times farther from Earth. This remarkable coincidence makes them appear nearly identical in size from our planet’s surface, enabling total solar eclipses.
Q: Which is hotter: the sun or moon?
The sun is dramatically hotter, with core temperatures reaching 27 million degrees Fahrenheit and surface temperatures around 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit. The moon’s temperature varies from about 260°F in sunlight to -280°F in darkness, with no internal heat source.
Q: How does the sun vs moon comparison affect Earth’s tides?
While both bodies influence tides, the moon’s gravitational effect is more significant due to its proximity to Earth. The sun’s gravitational pull also contributes, creating especially high “spring tides” when sun and moon align, and lower “neap tides” when they’re perpendicular.
Q: Will total solar eclipses always be possible?
No. The moon is gradually moving away from Earth at about 1.5 inches per year. In approximately 50 million years, the moon will appear too small to completely cover the sun, making total solar eclipses impossible and only annular eclipses observable.
Q: What’s the main chemical difference in the sun vs moon composition?
The sun consists primarily of hydrogen (91%) and helium (8.9%) in a plasma state, undergoing nuclear fusion. The moon is composed of solid rocky materials including silicate rocks, iron, and various minerals, with no atmosphere to speak of. These fundamental differences reflect their distinct origins and roles in our solar system but which celestial body do you find more fascinating, and why?